Healing varies, but it generally takes days to heal completely, and some people may take longer. It is essential that you drink plenty of fluids as you heal, even though it can be tough with the sore throat. Drink plenty of water and indulge in popsicles to start with. Until the pain dissipates stick with plain, easy-to-swallow foods, such as applesauce for example.
Graduate to pudding, yogurts, and frozen yogurt or ice cream until you are able to resume a healthy, normal diet. Even after a minor surgery, you need plenty of rest, avoid hard exercise for about to weeks that can cause you to breathe hard, making the throat raw. Once you do not require pain medication and can sleep through the night, your normal physical routines can continue. The tonsils and adenoids are masses of immune cells commonly found in lymph glands .
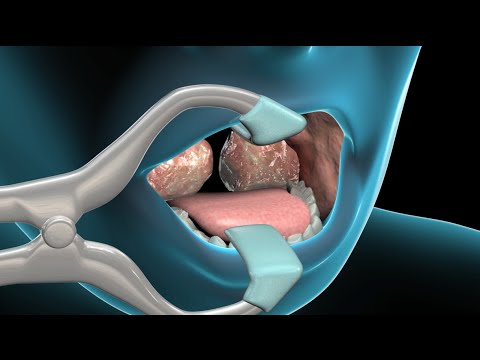
These tissues are located in the mouth and behind the nasal passages, respectively. Infected adenoids may become enlarged, obstruct breathing, cause ear infections, or other problems. Tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy are surgical procedures performed to remove the tonsils and adenoids. It is performed by an ears, nose, and throat surgeon in the operating room while the patient is under general anesthesia. The goal of surgery is to remove the tissue so that it won't continue to cause problems from infections or enlargement. The tonsil is removed from a pocket leaving a small raw area which heals over 1-2 weeks.
The area remains very sensitive and mild to severe pain is typical for 10 to 14 days. The tonsil may be removed by itself or at the same time as the adenoids. Adenoidectomy is uncommon in adults but if any concerns are present the adenoid tissue may be removed also. The inflammation results in sore throat, difficulty and pain with swallowing, fever and frequently changes of the appearance of the tonsils. It can be cause by viral and bacterial infections and the majority will resolve with time, even without antibiotic treatment. When tonsils are infected with a type of bacteria known as Group A Strep, antibiotics are given to prevent complications of the heart and kidneys.
When infections occur frequently or are more severe or chronic in nature surgery to remove the tonsils and adenoids may be beneficial. Tonsils that only get infected every once in awhile do not require any serious treatment and you can typically just ride it out. Once you have had the tonsils removed following surgery, you will not be inflicted with tonsillitis anymore. Additionally, removing the tonsils with surgery will also help people suffering from constant swollen tonsils and sleep apnea as other issues sleeping. Today, we atENT Specialistswould like to discuss the surgical experience and what you can expect. A tonsillectomy is the surgical removal of the tonsils, the two pads located at either side of the back of the throat.
The tonsils serve as part of the immune system, a first line of defense for pathogens entering the mouth or nose. Because of their function, they may become infected or inflamed and, in some cases, may require surgical removal. Tonsillectomies are more commonly performed on children than adults. A tonsillectomy may be necessary when an individual has recurring episodes of tonsillitis or an ongoing infection that has not healed with other treatment. Surgery may also be required if enlarged tonsils block airways, leading to sleep apnea, swallowing problems or difficulty eating. Rarely, a tonsillectomy may be performed to treat a malignancy of the tonsils.
Tonsillitis Tonsillitis is a contagious infection with symptoms of bad breath, snoring, congestion, headache, hoarseness, laryngitis, and coughing up blood. Tonsillitis can be caused acute infection of the tonsils, and several types of bacteria or viruses . There are two types of tonsillitis, acute and chronic.
Acute tonsillitis lasts from one to two weeks while chronic tonsillitis can last from months to years. If you have a sore throat or earache, you should take the painkillers that will be prescribed at the hospital. Make sure you follow the instructions on the packaging. Taking a dose half an hour before meals may help to make eating more comfortable. Please take these as recommended, remembering to complete the whole course, even if you feel completely well. You should stay at home for seven to 14 days after the operation.
Where possible, avoid contact with people who have colds, coughs or other infections. You should also avoid strenuous activities during this time. A tonsillectomy is the surgical removal of the tonsils. The tonsils are visible glands located in the back of your throat. Tonsils fight infection but can get infected and enlarged themselves. Frequent bouts of tonsillitis can lead to difficulty breathing, sleep apnea , difficulty eating, and ear infections.
Your doctor may recommend a tonsillectomy if you or your child suffer from any or all of these conditions. The tonsils are 2 small masses of tissue at the back of the throat. In some people, the tonsils become infected or enlarged. This can cause severe sore throats, snoring, or other problems. Tonsillectomy may be recommended if you have obstruction causing sleep apnea, or recurring, chronic, or severe infections.
Adult tonsillectomies are similar to the procedure thousands of children have every year. The surgeon will perform the procedure under general anesthesia. While the patient is asleep, the surgeon uses a small scalpel to remove the tonsils and sometimes the adenoids. The doctor will then monitor the patient for any complications. Speak with the doctor about any strange symptoms, as some risks come with surgery. Overall, surgery can stop the pain and discomfort that can come with constantly swollen, infected tonsils.
Your child's throat will be very sore for quite a while after surgery. Most children will have throat pain for 10 to 14 days after a tonsillectomy. The sore throat makes it difficult and painful to swallow.
However, it is very important that your child drink plenty of fluids after surgery. Your child will be given prescription pain medicine for the sore, throat but it will still take lots of encouragement to keep him or her drinking at home. The second kind of tonsillectomy involves removing most of the tonsil tissue but leaves a small amount of tonsil tissue behind to protect the side of the throat. This typically results much less pain after surgery and a shorter recovery. However, there is the possibility that in time tonsils will grow back and possibly become large enough to cause symptoms again.
This type of tonsillectomy is usually recommended for very young children with sleep apnea. The intracapsular tonsillectomy is not appropriate for children with lots of strep throat or tonsillitis. There are several post-operative problems that may arise. These include swallowing problems, vomiting, fever, throat pain, and ear pain.
Occasionally, bleeding from the mouth or nose may occur after surgery. If you have any bleeding, your surgeon should be notified immediately. It is also important to drink plenty of liquids after surgery to avoid dehydration. During laser ablation, a handheld laser device uses carbon dioxide to cut and destroy the tonsillar tissue.
This technique reduces tonsil volume and eliminates recesses that collect recurrent infectious bacteria. This procedure is recommended for chronic sufferers of tonsillitis, chronic sore throats, severe halitosis, or airway obstruction caused by enlarged tonsils. The laser tonsil ablation is performed in 15 to 20 minutes under local anesthesia.
The patient may experience minimal discomfort and may return to school or work the next day. After a few days, scabs will form where the incisions were in the mouth. The doctor may prescribe painkillers to help relieve rawness and soreness in the patient's throat.
It is imperative to drink lots of ice water and cold fluids after tonsil removal, but avoid drinking through straws, as it may be difficult. Eating soft foods and ice pops may help avoid irritation in the area. If the patient loses weight, they should try drinking nutritional beverages to add some calories to their diet. The first question many people ask is why would adults consider having their tonsils removed. In many cases, it's for the same reason as young children. If you've suffered from several infections over the past one to three years, such as strep throat or tonsillitis, you might be a candidate for a tonsillectomy.
It's often recommended for people who have an infection that gets better with antibiotics but comes back once the prescribed medication ends. ACTIVITY -It is advisable to rest at home for the first 48 hours. The more you move around, the sooner you will start to feel better.
Activity may be increased slowly, with a return to work after normal eating and drinking resumes, and pain medication is no longer required. Travel on airplanes or far away from a medical facility is not recommended for two weeks following surgery. Vigorous physical activity should be avoided for 14 days following tonsil surgery. Tonsillitis is an infection of the tonsils that can make your tonsils swell and give you a sore throat.
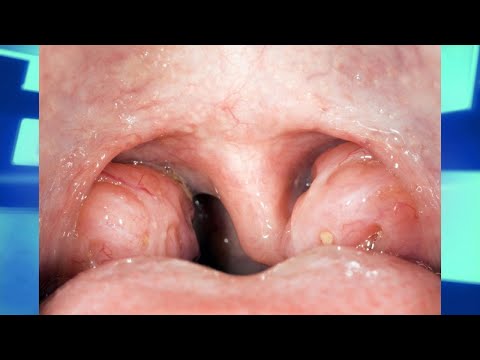
Frequent episodes of tonsillitis might be a reason you need to have a tonsillectomy. Other symptoms of tonsillitis include fever, trouble swallowing, and swollen glands around your neck. Your doctor may notice that your throat is red and your tonsils are covered in a whitish or yellow coating.
In other cases, antibiotics or a tonsillectomy might be necessary. Bleeding occurs in 1%-3% of patients after a tonsillectomy. Although it may occur at any time, it usually occurs 5-10 days after the surgery.
Dehydration and excessive activity increase the chances of postoperative bleeding. If bleeding occurs, the patient should try to remain calm and relaxed. Rinse the mouth out with cold water and rest with the head elevated. Rarely, it may require a trip back to the operating room for cauterization of the bleeding area under general anesthesia. In very rare situations, a blood transfusion may become necessary. Conversely, bleeding is rare following an adenoidectomy.
There may be some bleeding from the nose following surgery. If it occurs, pediatric Neosynephrine nose drops can be used. If it is persistent and bright red in color, call the doctor. It is often hard to predict who will recover quickly or who will have prolonged pain. Immediately after surgery, many patients report only minimal pain.
The next day the pain may increase and remain significant for several days. At one week following surgery, patients will often appear to relapse when their pain becomes significant again. They usually report pain in the ears, especially when they swallow. If bleeding is going to occur, this is the most common time.
This pain is usually the last time pain will be experienced. Overall, most patients will have recovered fully by two weeks after surgery. However, the patient will occasionally have throat tenderness with hot or spicy foods for up to 6 weeks postoperatively. Another common reason that children have their tonsils removed is because of frequent throat infections involving the tonsils . Although removing the tonsils will not prevent the common cold or even every sore throat, it will stop a child from getting tonsillitis again.
As opposed to the above office-based procedures, tonsillectomy/adenoidectomy is an outpatient surgery performed in the operating room under general anesthesia. Most patients require a recovery time at home of approximately one week but may continue to experience a sore throat for two weeks. The most common complication is bleeding, often occurring over a week after the surgery. You can expect to feel some pain in your throat, especially when swallowing that may make it difficult to eat and talk. Some patients also experience earache, a stiff jaw and bad breath.
In the meantime, your surgeon may prescribe a painkiller for your sore throat or you can use over-the-counter pain relief whilst keeping within the recommended dose. Your throat may feel sore for around 10 days after your tonsils are removed. The pain may get worse for a few days after the operation, before it gradually gets better. You'll need to take painkillers to help but don't take aspirin because it may cause problems with bleeding.
Always ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice and read the patient information leaflet that comes with your medicine. A tonsillectomy is an operation to remove your tonsils, which are small round lumps of tissue at the back of your throat. An adenoidectomy is a procedure to remove your adenoids, which are small lumps of tissue that lie where your throat meets the back of your nose.
If you have both your tonsils and adenoids removed, this is called an adenotonsillectomy. Tonsillar hypertrophy is abnormal enlargement of the tonsil tissue. Large tonsils are rarely the sole cause of snoring or sleep related problems in adults. The significance of the enlargement can sometimes be difficult to establish.